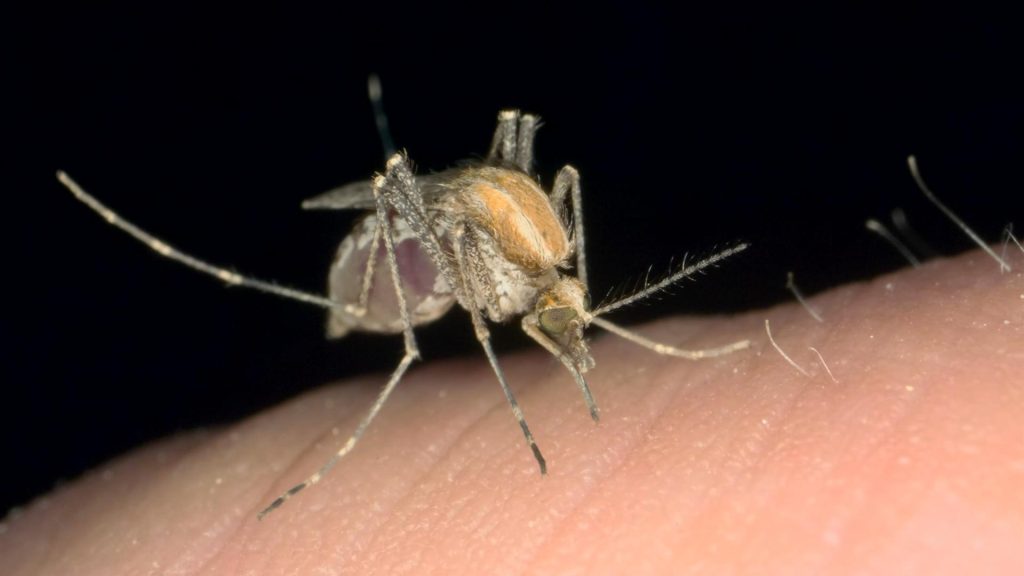
Understanding Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a viral disease transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. There are four types of dengue viruses: DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4. The symptoms typically begin 3 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever manifests in various ways, including:
- Common Dengue Fever: Symptoms include fever, body aches, headaches, and pain behind the eyes.
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: In addition to the above symptoms, this type involves plasma leakage from blood vessels, leading to decreased blood pressure.
- Dengue Shock Syndrome: A severe form of dengue hemorrhagic fever where blood pressure drops significantly, interrupting oxygen supply to body cells.
- Expanded Dengue Syndrome: The most severe form, affecting the brain, heart, liver, and kidneys.
Stages of Dengue Fever
- Febrile Phase: Lasts 2 to 7 days, characterized by red spots on the body, body pain, and headache.
- Critical Phase: Starts on the fourth or fifth day of fever, lasting 48 to 72 hours, and is extremely dangerous.
- Recovery Phase: Begins 2 to 3 days after the critical phase ends, where the patient gradually recovers.
Diagnosing Dengue Fever
Accurate diagnosis involves several tests:
- NS1: Positive within the first three days of fever.
- IgM: Positive from the sixth day of fever, lasting about a month.
- IgG: Indicates a past dengue infection.
- CBC, Platelet Count, SGPT, and SGOT: Important for assessing the patient’s condition.
Clinical Assessment
Clinical assessment involves evaluating the patient’s physical condition, blood pressure, stomach pain or vomiting, and bleeding.
Warning Signs and Hospitalization
Complications usually arise late in the fever or after the fever subsides. The patient should be monitored closely during this period. Hospitalization is necessary if:
- The patient is restless.
- Blood pressure decreases.
- Severe abdominal pain or vomiting occurs.
- There is water accumulation in the stomach or chest.
- The platelet count drops rapidly.
- There is bleeding.
Treatment for Hospitalized Patients
Treatment involves maintaining blood pressure with intravenous saline and close observation.
Preventing Dengue Fever in Children
- Eliminate Mosquito Breeding Sites: Destroy sources of stagnant water where mosquitoes breed.
- Use Mosquito Nets: Keep children inside mosquito nets day and night.
- Use Mosquito Repellents: Apply sprays, creams, or gels on children when outside. Use mosquito repellent belts or patches for younger children.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Dress children in full sleeves and full pants.
- Avoid Harmful Repellents: Use mosquito killer bulbs, electric killer lamps, and other safe mosquito repellers, keeping them out of children’s reach.
Additional Tips
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids.
- Rest: Ensure complete rest.
- Seek Medical Attention: If advised by a doctor, get admitted to the hospital promptly.
By following these guidelines, you can help prevent dengue fever and manage its symptoms effectively.